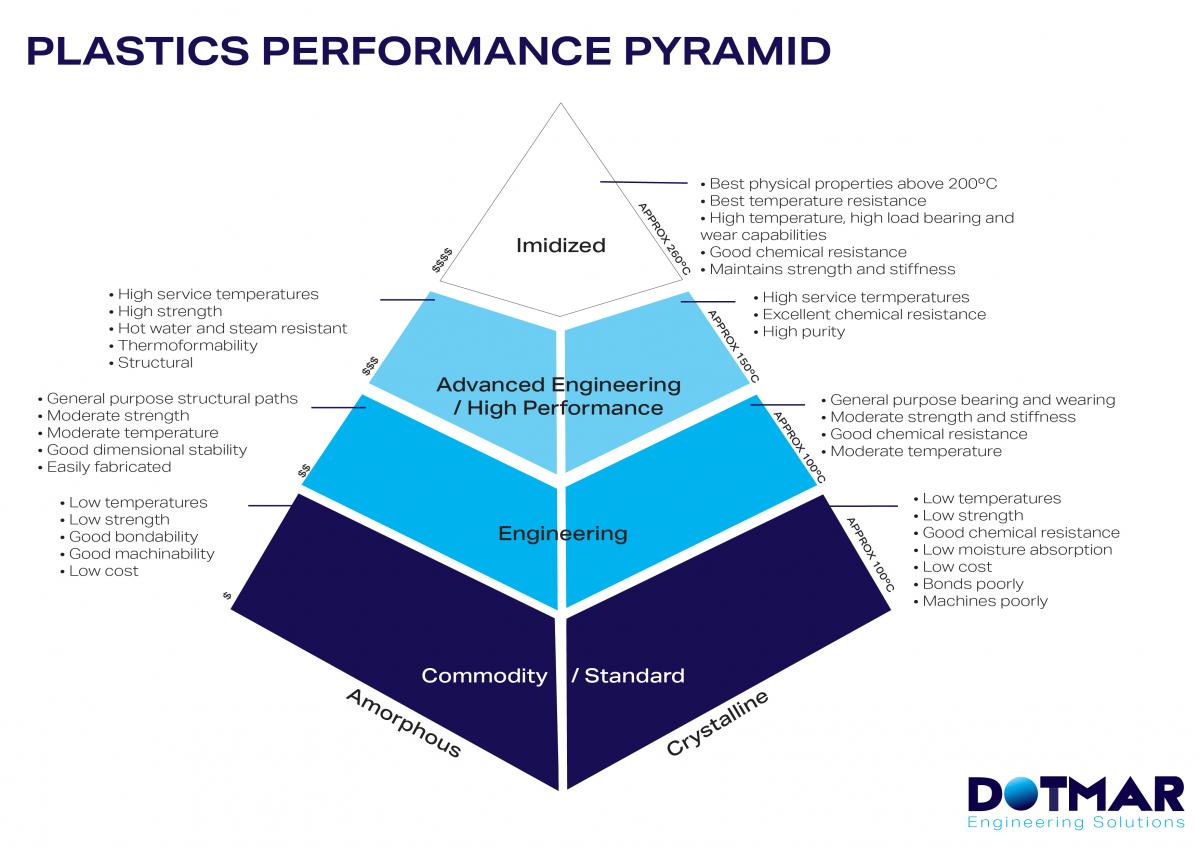
The plastic materials performance pyramid is an easy to use, at a glance material selection guide. It ranks the most common thermoplastics according to their temperature performance and strength.
Plastics can be broken into two ‘families’ – Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline. From there, four grades can be identified – commodity, engineering, high performance and imidized.
| Commodity Amorphous Plastics Characteristics: | Commodity Semi-Crystalline Plastics Characteristics: |
| · Low temperature resistance | · Low temperature resistance |
| · Low strength | · Low strength |
| · Good bondability | · Good chemical resistance |
| · Good machinability | · Low cost |
| · Low cost | · Bonds poorly |
| · Machines poorly |
|
| Engineering Amorphous Plastics Characteristics: | Engineering Semi-Crystalline Plastics Characteristics: |
| · Moderate temperature resistance | · Moderate temperature resistance |
| · Mid-strength | · Mid-strength or stiffness |
| · Good dimensional stability | · Low friction |
| · Good impact resistance | · Good wear resistance |
| · Easily fabricated |
· Good chemical resistance |
| High Performance Amorphous Plastics Characteristics: | High Performance Semi-Crystalline Plastics Characteristics: |
| · High temperature resistance | · High temperature resistance |
| · High strength | · High strength |
| · Good stiffness | · Excellent chemical resistance |
| · Resistant to hot water and steam | · High purity |
| · Thermoformable | · Electrical properties |
| · Structural |
|
| Imidized Plastics Characteristics: | |
| · Best physical properties above 204ºC | |
| · Best temperature resistance | |
| · High load bearing capabilities | |
| · High wear resistance | |
| · Good chemical resistance | |
| · Maintains strength and stiffness |